Updated: January 22, 2024
How Long Until a Tooth Infection Kills You
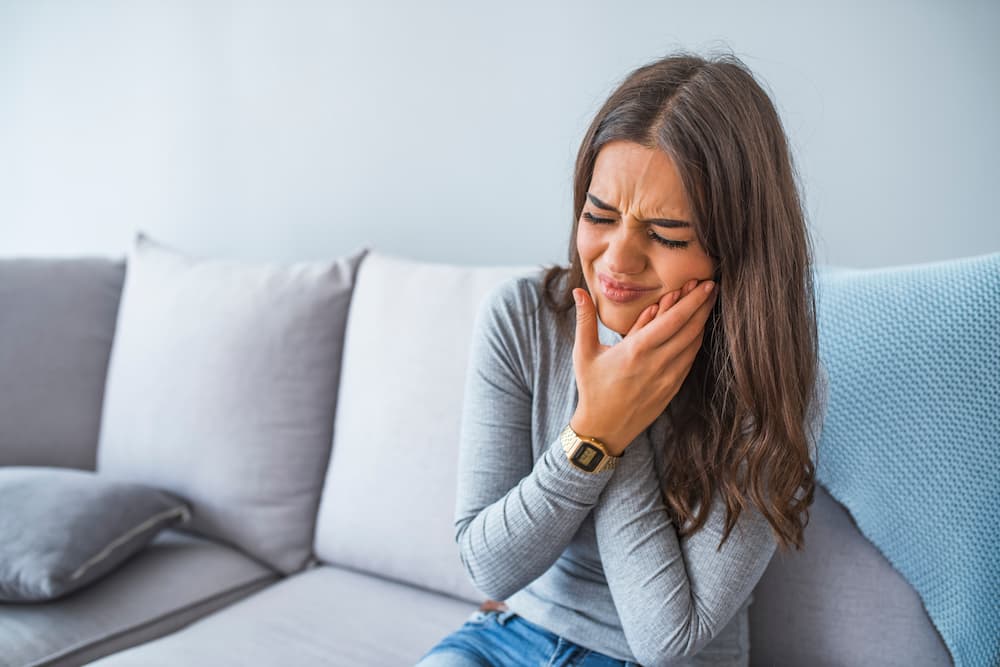
How long until a tooth infection kills you? It is almost possible to die from a tooth infection alone. Death commonly occurs when the bacterial infection spreads to other organs, where it can cause complications. The transition from a simple dental infection to a complication takes several weeks or months.
Ingenious Dentistry explains what a tooth infection is and how it can kill you. Find out the tell-tale signs of dental infection and how to get it treated before it advances to deadly complications.
What is a Tooth Infection?
It is an infection that affects a tooth’s pulp. Like many other dental problems, a tooth infection can affect anyone. Nevertheless, the infection is more prevalent in some groups, such as seniors and individuals with chipped or broken teeth. People with poor oral hygiene also have a higher risk of getting a tooth infection.
Signs of an Infected Tooth
Pain is the most obvious sign of an infected tooth. The pain can be throbbing or constant and usually gets worse when chewing. Other common signs that indicate a possible tooth infection include:
- Swelling in the face, gums, or cheek
- Sensitivity to hot or cold food
- Pus around the affected tooth
- Bad mouth odor
- Fever
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Difficulty opening your mouth
- Trouble chewing
Dentists classify dental infections into three types which are periodontal, gingival, and periapical. Periodontal tooth infection affects the gums and supporting bone. Gingival disease affects the gums and teeth. On the other hand, the periapical infection affects the tip of the tooth root.
Can a Tooth Infection Kill You?
Dental infection can lead to death when left untreated. The infection spreads to the heart, sinuses, and bloodstream, where it causes further complications. How long until a tooth infection kills you?
It depends on the type of complication you get. Some medical issues, like sepsis, can kill you within 28 days. Other conditions can take a couple of months to cause death. Some of these tooth-infection-related issues that can kill include:
- Sepsis. The bacteria that cause dental infection can enter the bloodstream if not treated. Upon entering the bloodstream, this bacteria can cause sepsis.
- Osteomyelitis. Osteomyelitis occurs when an untreated dental infection spreads to the jawbone. This complication can cause systemic infection or sepsis.
- Brain abscess. Sometimes the untreated tooth infection can spread to the brain and cause a brain abscess. The abscess can lead to brain damage.
- Endocarditis. Endocarditis affects the lining and valves of your heart. This disease can cause heart failure and, subsequently, death.
- Mediastinitis. An untreated dental infection can also affect the mediastinum, the area between the lungs. The condition can trigger or affect the respiratory system.
- Ludwig’s angina. A tooth infection can also cause Ludwig’s angina, a disease of the floor of the mouth. Ludwig’s angina can cause further complications, such as respiratory problems and sepsis.
Preventing Tooth Infection Through Routine Dental Visits
Can a tooth infection kill you? Although an untreated tooth infection can kill, you can reduce the risk by simply having routine dental checkups. During these exams, your Houston dentist will examine your teeth and gums to detect early signs of a tooth infection.
After a check-up, your dentist will recommend fillings, root canals, or extractions to help contain the infection. The dentist will also clean your teeth to remove plaque and tartar, the significant causes of tooth infection. At Ingenious Dentistry, we recommend seeing your dentist every six months.
Choose Ingenious Dentistry for Peace of Mind!
Our practice, Ingenious Dentistry, has served Houston, TX, for 30 years. We specialize in all dental procedures, including cosmetic dentistry and general dentistry. Furthermore, Ingenious Dentistry provides emergency dental care to patients with issues like severe tooth pain.
IMG Credit: Dragana Gordic